Gestational diabetes is a type of diabetes that occurs during pregnancy. This condition affects around 3 to 20 percent of pregnant women and can have serious consequences for both mother and baby if left untreated. Different diet plans are available, like snacks for gestational diabetes. Understanding what gestational diabetes is, its causes, and how it can be managed is important for expectant mothers and their healthcare providers.
What is gestational diabetes?
Gestational diabetes is a condition in which high blood sugar levels are detected during pregnancy. It is caused by the increased hormone levels in the body that make it more difficult for insulin to work properly. Insulin is the hormone responsible for regulating blood sugar levels.
Causes of gestational diabetes
The exact cause of gestational diabetes is unknown, but it is believed to be related to hormonal changes that occur during pregnancy. The placenta produces hormones that help the baby grow and develop, but these hormones can also make it more difficult for insulin to work effectively. This can result in high blood sugar levels, which can increase the risk of gestational diabetes.
Risk factors for gestational diabetes
Women who are at a higher risk of developing gestational diabetes include those who:
- Are overweight or obese
- Have a family history of diabetes
- Have had gestational diabetes in a previous pregnancy
- Have high blood pressure or cholesterol levels
- Are over the age of 25
Symptoms of gestational diabetes
Gestational diabetes often has no symptoms, which is why it is important for women to be tested for the condition during pregnancy. However, some women may experience increased thirst, frequent urination, fatigue, and blurred vision.
Diagnosing gestational diabetes
Gestational diabetes is usually diagnosed through a blood test during pregnancy. The test is typically done between 24 and 28 weeks of pregnancy. Women who have a high risk of developing gestational diabetes may be tested earlier in their pregnancy.
Managing gestational diabetes
The goal of gestational diabetes management is to keep blood sugar levels within a normal range. This can be achieved through a combination of diet, exercise, and medication.
Dietary changes
Women with gestational diabetes should work with a registered dietitian to develop a meal plan that will help them manage their blood sugar levels. This typically involves eating a balanced diet that includes plenty of fruits and vegetables, lean proteins, and whole grains. Women should also aim to limit their intake of sugar and carbohydrates.
Physical activity
Physical activity can help women with gestational diabetes manage their blood sugar levels. It is recommended that women with gestational diabetes engage in 30 minutes of moderate physical activity, such as brisk walking, on most days of the week.
Medications
If dietary changes and physical activity are not enough to control blood sugar levels, medication may be prescribed. The most common medications used to treat gestational diabetes are insulin injections.
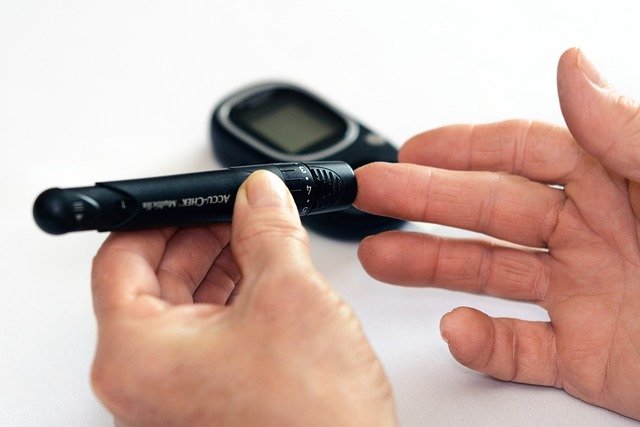
Monitoring blood sugar levels
Women with gestational diabetes will need to monitor their blood sugar levels regularly. This can be done using a blood glucose meter, which allows women to measure their blood sugar levels at home. Women should work with their healthcare provider to determine how often they need to check their blood sugar levels.