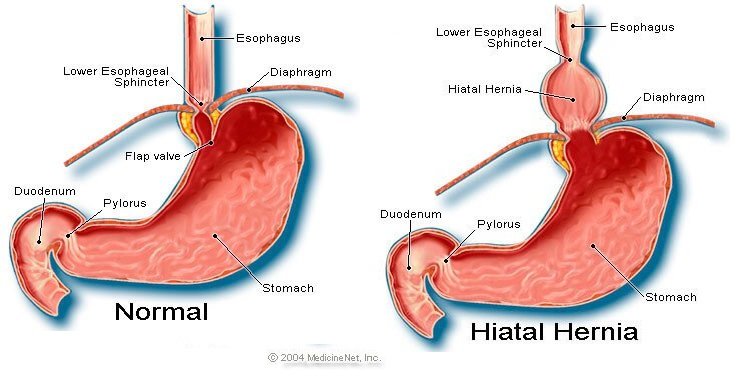
A Hiatal hernia occurs when part of the stomach pushes into the chest through a passage or opening known as (hiatus) in the diaphragm. The diaphragm separates the lungs from the abdomen.
A hiatal hernia rarely has any apparent symptoms, but it can cause a situation called –GORD. GORD is when the stomach acid enters into the esophagus and therefore prevents it from working correctly.
When the esophagus becomes overly irritated because of its exposure to stomach acid, symptoms like chest pain, heartburn, swallowing problems and sour taste in the mouth becomes common.
Causes a Hiatal Hernia
The cause of a hiatus hernia is not clear, but it may be as a result of the diaphragm becoming thin and weak due to aging or from intense pressure on the abdomen.
Who is affected?
Everyone can be affected by a hiatus hernia, but the people who are more likely to get it are those who are above the age of 50, obese or pregnant. There is also a rare type of a hiatal hernia that is common with babies, and it is caused by a defect in the diaphragm
Types of a hiatal hernia
There are two major types of a hiatus hernia. They are as follows.
1. The Para-esophageal hiatus hernia – This is when a part of the stomach pushes through a gap in the diaphragm right next to the esophagus.
2. Sliding hiatus hernia – This is very common, and it occurs when the hernias move either downward or upward in the chest region.
Comlications from a hiatal hernia
Complications from a hiatal hernia are not common but can be very serious when they occur. Below, are some common complication that is associated with a hiatal hernia.
Esophageal ulcers
This occurs due to the damage the stomach acid has on the lining of the esophagus which ultimately leads to the formation of an Ulcer. The ulcer bleeds from time to time, causing serious pain and difficulty in swallowing. Ulcers can be treated by the use of medicines called ANTACIDS.
Oesophageal stricture
Continuous damage to the lining of the esophagus will lead to the formation of a scared tissue. If the tissue is not treated, it will build up and make the esophagus become narrow. This condition is known as an esophageal stricture.
An oesophageal stricture usually makes swallowing very difficult. A common way to treat this condition is through the use of a tiny balloon to widen the esophagus.
Barrett’s esophagus
The continuous irritation of the esophagus by the stomach acid can lead to a change in the cells of the lower esophagus. This condition is known as Barrett’s esophagus.
Barrette’s esophagus does not manifest any noticeable symptoms, but they increase the risk of esophageal cancer.
Strangulated Hernia
In rare cases, a hiatus hernia may cause a part of the stomach to push up into the esophagus. In this situation, the stomach acid does not enter the esophagus, but it increases the risk of a hernia to become strangulated. When this occurs, an emergency surgery is required.
Treatment of a Hiatal Hernia
A Hiatal hernia cure is possible without surgery; all it requires is a change in the lifestyle of those who suffer from it.
Below are some simple and effective ways people who suffer a Hiatal hernia can treat it naturally.
- Avoid drinking at night.
- Stop eating food that makes the symptoms worse.
- Avoid caffeine, tomatoes, acidic drinks or food, some fruit juice, and fatty foods especially if they make the symptoms worse.
- Eat in small chunks throughout the day and avoid eating a large meal.
- Avoid lying down after drinking or eating.
- Do not bend over especially when you are eating or drinking.
- Raise the head of your bed by 8 inches (20cm)
- Losing weight is a very effective way to reduce the frequency and severity of the symptoms.
- Avoid degrading habits like smoking and the use of tobacco because they affect the digestive system negatively.
Medication for Hiatus Hernia
They are some medications that can be used to treat the symptom of a Hiatus Hernia.
- Antacids – They can either be chewed or swallowed. They neutralize the stomach acid when it reaches the esophagus making it less acidic
- Alginates – They help in the production of a protective coating in the lining of the stomach.
- H2-receptor antagonists – They help to block the effects of the chemical “histamine” which the body uses to produce stomach acid.